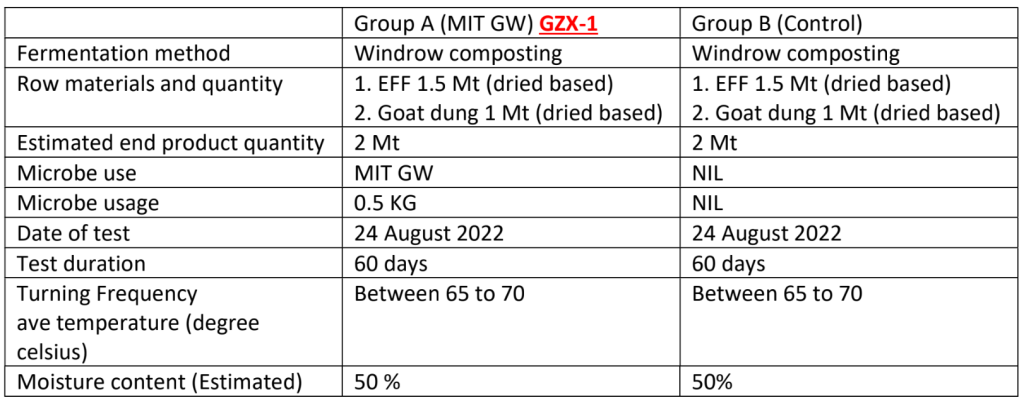
MIT Sabah Composting Test Batch 1 : Fiber and Goat Dung
Materials used
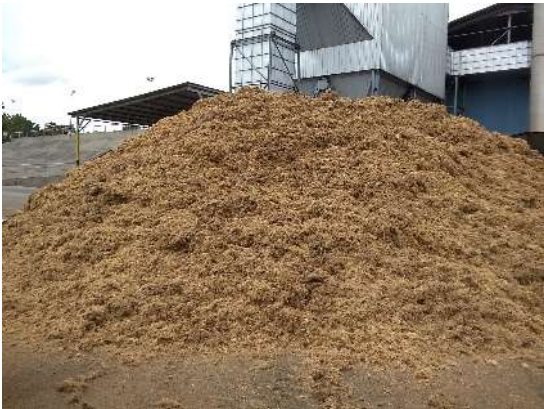

Oil palm empty fruit fiber (EFF)

Goat dung
Test protocol
Note:
Group A : Oil palm EFF (Empty Fruit Fiber) with goat dung mix with MIT GW
Group B : Oil palm EFF with goat dung without microbe (control)
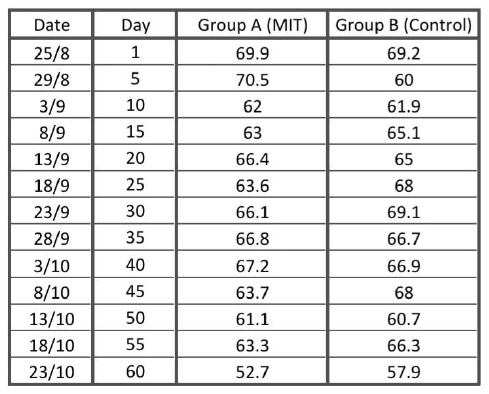
Temperature Record
Day 0
Group A

Group B

Day 60
Group A

Group B

Temperature Chart

Comparison and Observation (day 60)
Compare items
Temperature
Appearance
Decomposition
Decomposition
Odours
Toughness
Moisture
Group A and B

No significant difference
No significant difference in colour and outlook.
20 days screening result
Group A 51 %
Group B 46 %
Group A screened out 10.8% more than Group B.
40 days screening result
Group A 30 %
Group B 27.9 %
Group A screened out 7.5% more than Group B.
60 days screening result
Group A 37.3 %
Group B 28.2 %
Group A screened out 32.2% more than Group B.

Group B has significantly more fungal grown than Group A.
No significant difference
No significant difference
Group A (MIT GW)

Average Temperature: 66.8°C


Gross weight : 6.2 kg
Net weight : 2.1 kg
Percentage : 51%

Gross weight : 7.05 kg
Net weight : 2.15 kg
Percentage : 30%

Gross weight : 7.50 kg
Net weight : 2.8 kg
Percentage : 37.3%

1st batch fungals grown
(day 21)

2nd batch fungals grown
(day 35)

3rd batch fungals grown
(day 42)

4th batch fungals grown
(day 51)
Less smell
Softer
Group B (Control)

Average temperature: 66.7°C


Gross weight : 6.8 kg
Net weight : 2.15 kg
Percentage : 46%

Gross weight : 6.1 kg
Net weight : 1.7 kg
Percentage : 27.9%

Gross weight : 7.8 kg
Net weight : 2.2 kg
Percentage : 28.2%

1st batch fungals grown
(day 21)

2nd batch fungals grown
(day 35)

3rd batch fungals grown
(day 42)

4th batch fungals grown
(day 51)
More smell
Harder
Materials list
Oil palm empty fruit fibre (EFF)

Goat dung

MIT GW (fermentation microbe)

Conclusions
After 60 days of fermentation, the experimental results are as follows:
1. Both groups have started to drop in temperature. The temperature of Group A (MIT) was 5 degrees lower than that of Group B (control). This shows that the action of fermenting microbes is faster than that of natural fermentation.
2. Group B had significantly more fungal then Group A. This proves that MIT fermenting microbes can effectively inhibit other unfriendly microbe.
3. There was no significant difference in the appearance of the finished products after sieving between the two groups, but the fiber structure of Group A was softer than Group B and easier to tear by hand.
4. The fermentation period must be extended for at least half a month, in order to lower the temperature to 40 degrees Celsius.
5. It is recommended to shred the crude fiber before fermentation, which can effectively shorten the fermentation period.
